7 Group sequential design boundary with weighted logrank test
7.1 Group sequential design boundary calculation strategy
In the last chapter, we pre-specified boundary derived from gsDesign. Therefore, the Type I error may be inflated because the information fraction is different for different WLR.
In this chapter, we calculate boundaries based on the error spending approach following Gordon Lan and DeMets (1983).
The spending function has been implemented in gsDesign.
-
gsDesign::sfLDOF()(O’Brien-Fleming bound approximation) or other functions starting withsfin gsDesign. - The boundary family approach (Pocock 1977; O’Brien and Fleming 1979; Wang and Tsiatis 1987).
There are other ways to derive boundaries but will not be covered:
- Conditional power (Lachin 2005).
7.2 Types of error probability
There are 6 different types of error probability that have been implemented in gsdmvn. In this training material, we focus on test.type = 4.
-
test.typeargument in gsDesign - Upper bound:
- \(\alpha_k(0) = \text{Pr}(\cap_{i=1}^{i=k-1} a_i < Z_i < b_i, Z_k > b_k \mid H_0)\)
- \(\alpha_k^{+}(0) = \text{Pr}(\cap_{i=1}^{i=k-1} a_i < Z_i < b_i, Z_k > b_k \mid H_0)\) (ignore lower bound)
- Lower bound:
- \(\beta_k(0) = \text{Pr}(\cap_{i=1}^{i=k-1} a_i < Z_i < b_i, Z_k < a_k \mid H_0)\) (under null)
- \(\beta_k(\delta) = \text{Pr}(\cap_{i=1}^{i=k-1} a_i < Z_i < b_i, Z_k < a_k \mid H_1)\) (under alternative)
test.typeUpper bound Lower bound 1 \(\alpha_k^{+}(0)\) None 2 \(\alpha(0)\) \(\beta_k(0)\) 3 \(\alpha_k(0)\) \(\beta_k(\delta)\) 4 \(\alpha_k^{+}(0)\) \(\beta_k(\delta)\) 5 \(\alpha(0)\) \(\beta_k(0)\) 6 \(\alpha^{+}(0)\) \(\beta_k(0)\) -
test.type = 1, 2, 5, 6: sample size boundaries can be computed in a single step. -
test.type = 3andtest.type = 4: sample size and boundaries are set simultaneously using an iterative algorithm. - This section and last section focus on
test.type = 4.
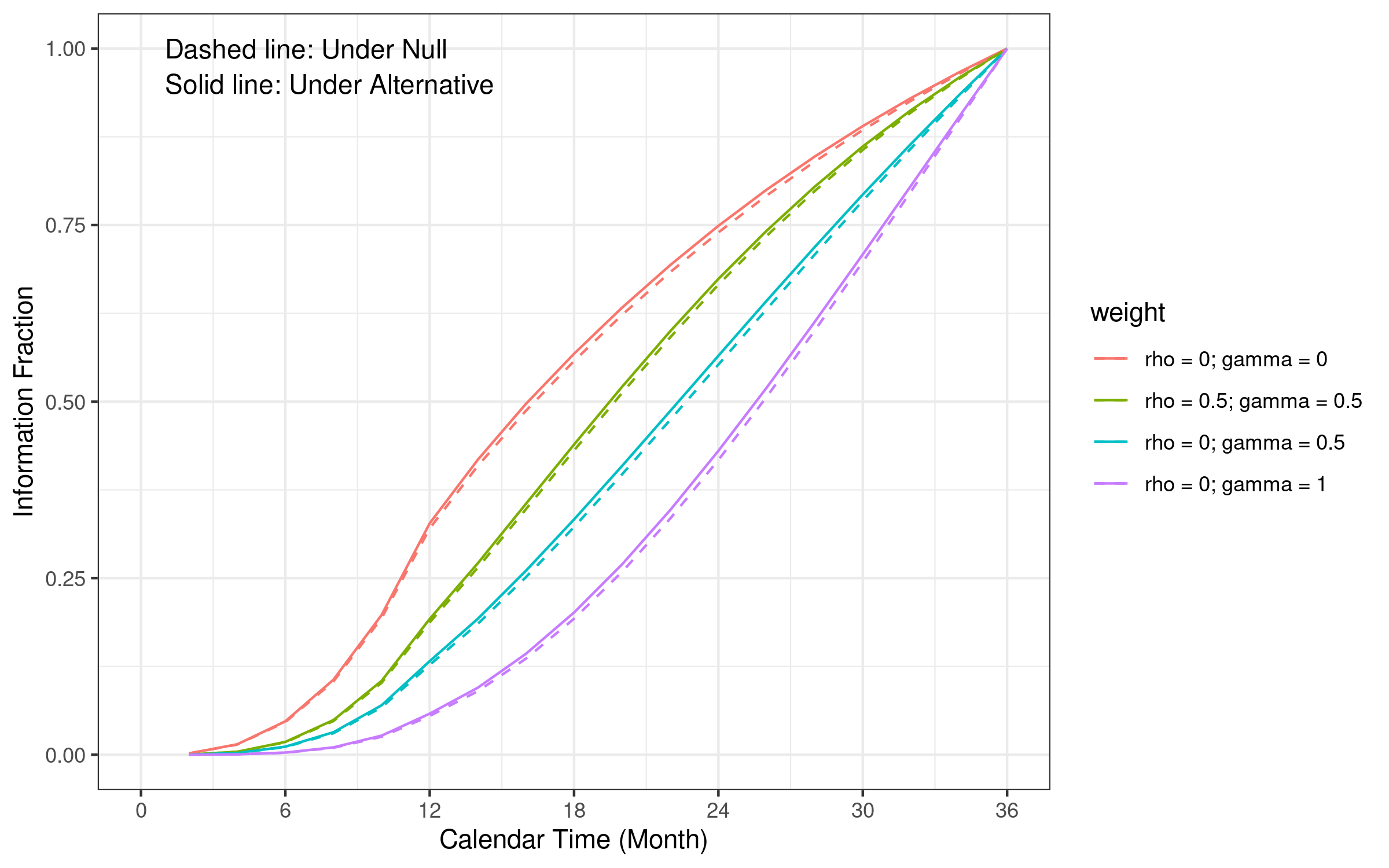
7.3 Information fraction
Under the same design assumption, information fraction is different from different weight parameters in WLR.
We continue using the same example scenario in the last chapter.
7.4 Spending function based on information fraction
The spending function is based on information fraction. We considered the Lan-DeMets spending function to approximate an O’Brien-Fleming bound Gordon Lan and DeMets (1983). (gsDesign::sfLDOF()).
Here, \(t\) is information fraction in the formula below.
\[f(t; \alpha)=2-2\Phi\left(\Phi^{-1}\left(\frac{1-\alpha/2}{t^{\rho/2}}\right)\right)\]
7.4.1 Spending function in gsDesign
After the spending function is selected, we can calculate the lower and upper bound of a group sequential design.
In test type 4, the lower bound is non-binding. So we set lower bound are all -Inf when we calculate the probability to cross upper bound.
We first use the alpha spending function to determine the upper bound of a group sequential design
- Let \((a_k, b_k), k=1,\dots, K\) denotes the lower and upper bound.
For gsDesign with logrank test, we considered equal increments of information fraction at t = 1:3 / 3 is.
The upper bound and lower bound based on the Lan-DeMets spending function can be calculated using gsDesign::sfLDOF().
- Upper bound:
alpha_spend <- gsDesign::sfLDOF(alpha = 0.025, t = 1:3 / 3)$spend
alpha_spend
#> [1] 0.0001035057 0.0060483891 0.0250000000- Lower bound:
beta_spend <- gsDesign::sfLDOF(alpha = 0.2, t = 1:3 / 3)$spend
beta_spend
#> [1] 0.02643829 0.11651432 0.20000000We considered different WLR tests with weight functions: \(FH(0, 0)\), \(FH(0.5, 0.5)\), \(FH(0, 0.5)\), \(FH(0, 1)\)
weight_fun <- list(
function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 0)
},
function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0.5, gamma = 0.5)
},
function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 0.5)
},
function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 1)
}
)
# Weight name
weight_name <- data.frame(rho = c(0, 0.5, 0, 0), gamma = c(0, 0.5, 0.5, 1))
weight_name <- with(weight_name, paste0("rho = ", rho, "; gamma = ", gamma))For test type 4, the alpha and beta is defined as below.
-
\(\alpha_k^{+}(0) = \text{Pr}(\cap_{i=1}^{i=k-1} a_i < Z_i < b_i, Z_k > b_k \mid H_0)\) (ignore lower bound)
- \(\alpha_k^{+}(0)\) is calculated under the null. It is the same for different sample size.
-
\(\beta_k(\delta) = \text{Pr}(\cap_{i=1}^{i=k-1} a_i < Z_i < b_i, Z_k < a_k \mid H_1)\) (under alternative)
- \(\beta_k(\delta)\) is calculated under the alternative. It depends on the sample size.
- Iteration is required to find proper sample size and boundary.
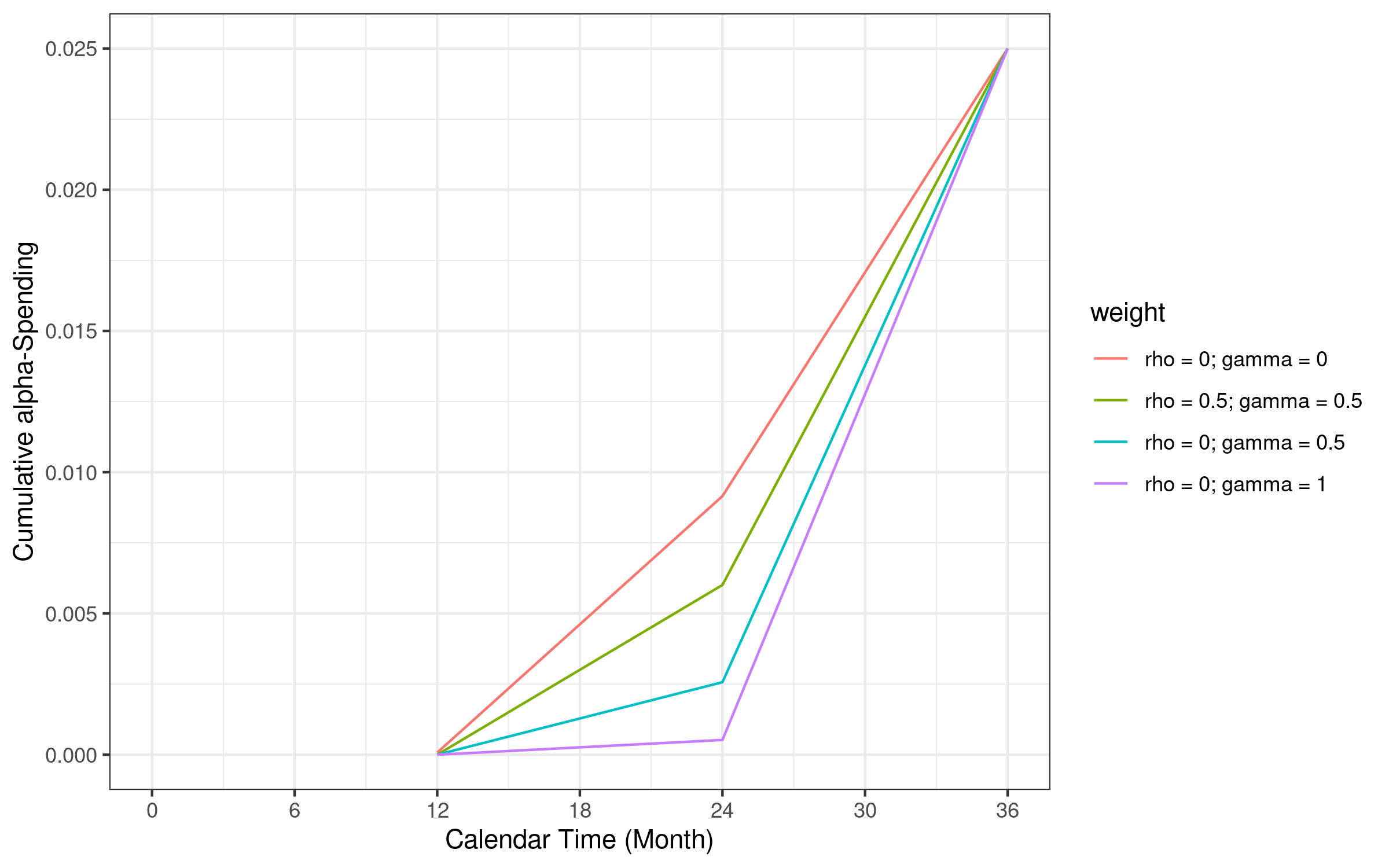
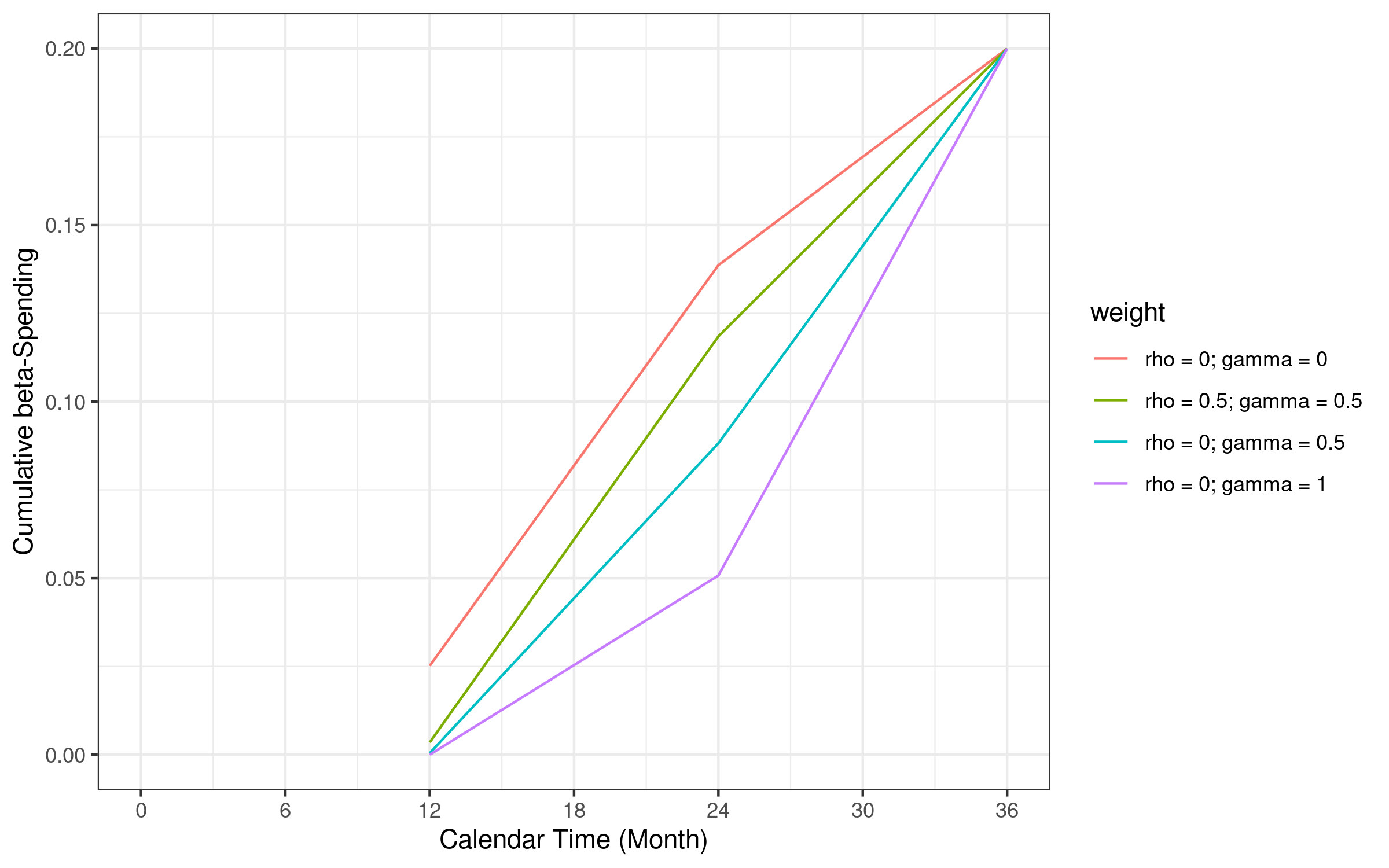
The table below provide the cumulative alpha and beta at different analysis time for each WLR test.
we draw the Alpha spending (\(\alpha=0.025\)) function based on information fraction at 12, 24 and 36 months
Similarly, we draw the Beta spending (\(\beta=0.2\)) function based on information fraction at 12, 24 and 36 months
analysisTimes <- c(12, 24, 36)
gs_spend <- lapply(weight_fun, function(weight) {
tmp <- gsdmvn::gs_info_wlr(
enrollRates, failRates,
analysisTimes = analysisTimes,
weight = weight
)
tmp %>% mutate(
theta = abs(delta) / sqrt(sigma2),
info = info / max(info),
info0 = info0 / max(info0),
alpha = gsDesign::sfLDOF(alpha = 0.025, t = info0)$spend,
beta = gsDesign::sfLDOF(alpha = 0.20, t = info)$spend
)
})names(gs_spend) <- weight_name
bind_rows(gs_spend, .id = "weight") %>%
select(weight, Time, alpha, beta) %>%
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, digits = 3)
#> weight Time alpha beta
#> 1 rho = 0; gamma = 0 12 0.000 0.025
#> 2 rho = 0; gamma = 0 24 0.009 0.139
#> 3 rho = 0; gamma = 0 36 0.025 0.200
#> 4 rho = 0.5; gamma = 0.5 12 0.000 0.003
#> 5 rho = 0.5; gamma = 0.5 24 0.006 0.118
#> 6 rho = 0.5; gamma = 0.5 36 0.025 0.200
#> 7 rho = 0; gamma = 0.5 12 0.000 0.000
#> 8 rho = 0; gamma = 0.5 24 0.003 0.088
#> 9 rho = 0; gamma = 0.5 36 0.025 0.200
#> 10 rho = 0; gamma = 1 12 0.000 0.000
#> 11 rho = 0; gamma = 1 24 0.001 0.051
#> 12 rho = 0; gamma = 1 36 0.025 0.2007.5 Lower and upper bound
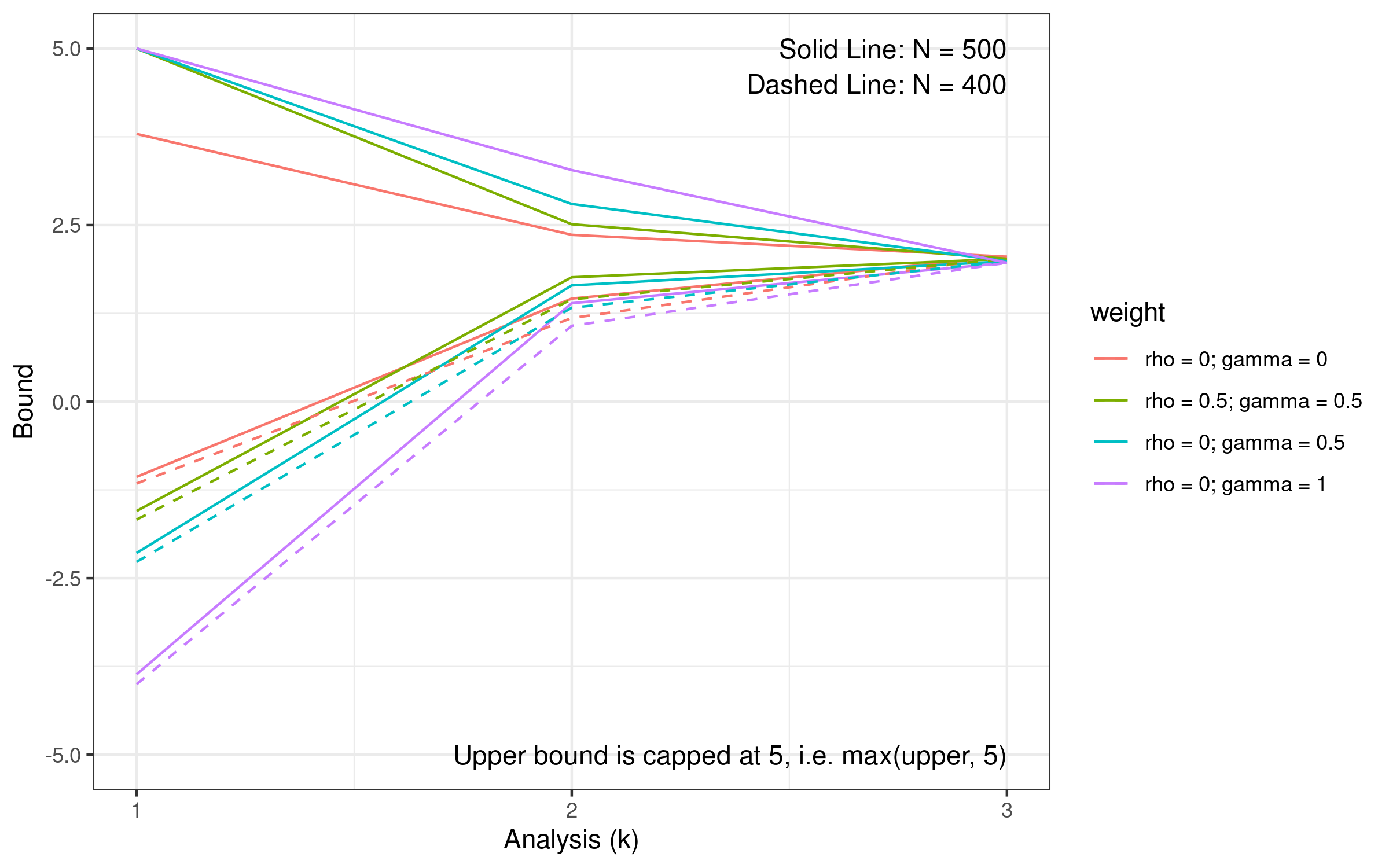
Let’s calculate the lower and upper bound of the first interim analysis.
- First interim analysis upper bound: \(\text{Pr}(Z_1 > b_1 \mid H_0)\)
-qnorm(gs_spend[[1]]$alpha[1])
#> [1] 3.790778- First interim analysis lower bound \(\text{Pr}(Z_1 < b_1 \mid H_1)\)
The lower bound is calculated under alternative hypothesis and depends on sample size.
The figure below illustrates the lower and upper bound in different sample size
- A larger sample size has a larger lower bound (solid line compared with dashed line)
- Iteration is required to find proper sample size and boundary.
7.6 Sample size calculation logrank test based on AHR
- Sample size
x <- gsdmvn::gs_design_ahr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
ratio = ratio, alpha = alpha, beta = beta,
upper = gs_spending_bound,
lower = gs_spending_bound,
upar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = alpha),
lpar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = beta),
analysisTimes = analysisTimes
)$bounds %>%
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, digits = 2)
x
#> # A tibble: 6 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 12 379. 81.4 3.77 0 0.84 0.17
#> 2 2 Upper 24 379. 187. 2.35 0.47 0.71 0.34
#> 3 3 Upper 36 379. 251. 2.01 0.8 0.68 0.38
#> 4 1 Lower 12 379. 81.4 -1.19 0.02 0.84 0.17
#> 5 2 Lower 24 379. 187. 1.13 0.14 0.71 0.34
#> 6 3 Lower 36 379. 251. 2.01 0.2 0.68 0.38
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>- Simulation results based on 10,000 replications.
#> n t events ahr lower upper
#> 1 379 12 81.23 0.86 0.02 0.00
#> 2 379 24 186.50 0.72 0.13 0.48
#> 3 379 36 251.05 0.69 0.19 0.81- Type I error
gsdmvn::gs_power_npe(
theta = rep(0, length(analysisTimes)),
info = x$info0[x$Bound == "Upper"],
upar = x$Z[x$Bound == "Upper"],
lpar = rep(-Inf, 3)
)$Probability[1:length(analysisTimes)]
#> [1] 8.162377e-05 9.415389e-03 2.505418e-02- Compared with fixed design
gsdmvn::gs_design_ahr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
ratio = 1, alpha = 0.025, beta = 0.2,
upar = -qnorm(0.025),
lpar = -qnorm(0.025),
analysisTimes = 36
)$bounds
#> # A tibble: 1 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 36 328. 217. 1.96 0.8 0.683 0.381
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>7.7 Sample size calculation logrank test based on WLR \(FH(0, 0)\)
- Sample size
x <- gsdmvn::gs_design_wlr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
ratio = ratio, alpha = alpha, beta = beta,
weight = function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 0)
},
upper = gs_spending_bound,
lower = gs_spending_bound,
upar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = alpha),
lpar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = beta),
analysisTimes = analysisTimes
)$bounds %>%
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, digits = 2)
x
#> # A tibble: 6 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 12 377. 81 3.79 0 0.84 0.17
#> 2 2 Upper 24 377. 186. 2.36 0.46 0.72 0.33
#> 3 3 Upper 36 377. 250. 2.01 0.8 0.68 0.38
#> 4 1 Lower 12 377. 81 -1.18 0.03 0.84 0.17
#> 5 2 Lower 24 377. 186. 1.15 0.14 0.72 0.33
#> 6 3 Lower 36 377. 250. 2.01 0.2 0.68 0.38
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>- Simulation results based on 10,000 replications.
#> n t events ahr lower upper
#> 1 378 12 80.98 0.86 0.03 0.00
#> 2 378 24 186.10 0.72 0.14 0.47
#> 3 378 36 250.33 0.69 0.20 0.80- Type I error
gsdmvn::gs_power_npe(
theta = rep(0, length(analysisTimes)),
info = x$info0[x$Bound == "Upper"],
upar = x$Z[x$Bound == "Upper"],
lpar = rep(-Inf, 3)
)$Probability[1:length(analysisTimes)]
#> [1] 7.532364e-05 9.164191e-03 2.497474e-02- Compared with fixed design
gsdmvn::gs_design_wlr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
weight = function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 0)
},
ratio = 1, alpha = 0.025, beta = 0.2,
upar = -qnorm(0.025),
lpar = -qnorm(0.025),
analysisTimes = 36
)$bounds
#> # A tibble: 1 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 36 324. 215. 1.96 0.8 0.683 0.381
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>7.8 Sample size calculation \(FH(0, 1)\)
- Sample size
x <- gsdmvn::gs_design_wlr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
ratio = ratio, alpha = alpha, beta = beta,
weight = function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 1)
},
upper = gs_spending_bound,
lower = gs_spending_bound,
upar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = alpha),
lpar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = beta),
analysisTimes = analysisTimes
)$bounds %>%
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, digits = 2)
x
#> # A tibble: 6 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 12 287. 61.6 Inf 0 0.73
#> 2 2 Upper 24 287. 141. 3.28 0.16 0.64
#> 3 3 Upper 36 287. 190. 1.96 0.8 0.62
#> 4 1 Lower 12 287. 61.6 -4.18 0 0.73
#> 5 2 Lower 24 287. 141. 0.66 0.05 0.64
#> 6 3 Lower 36 287. 190. 1.96 0.2 0.62
#> # ℹ 3 more variables: theta <dbl>, info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>- Simulation results based on 10,000 replications.
#> n t events ahr lower upper
#> 10 287 12 61.64 0.77 0.00 0.00
#> 11 287 24 141.41 0.65 0.05 0.17
#> 12 287 36 190.20 0.63 0.20 0.80- Type I error
gsdmvn::gs_power_npe(
theta = rep(0, length(analysisTimes)),
info = x$info0[x$Bound == "Upper"],
upar = x$Z[x$Bound == "Upper"],
lpar = rep(-Inf, 3)
)$Probability[1:length(analysisTimes)]
#> [1] 0.0000000000 0.0005191052 0.0251730067- Compared with fixed design
gsdmvn::gs_design_wlr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
weight = function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 1)
},
ratio = 1, alpha = 0.025, beta = 0.2,
upar = -qnorm(0.025),
lpar = -qnorm(0.025),
analysisTimes = 36
)$bounds
#> # A tibble: 1 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 36 264. 175. 1.96 0.8 0.617 1.08
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>7.9 Sample size calculation \(FH(0, 0.5)\)
- Sample size
x <- gsdmvn::gs_design_wlr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
ratio = ratio, alpha = alpha, beta = beta,
weight = function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 0.5)
},
upper = gs_spending_bound,
lower = gs_spending_bound,
upar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = alpha),
lpar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = beta),
analysisTimes = analysisTimes
)$bounds %>%
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, digits = 2)
x
#> # A tibble: 6 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 12 288. 61.9 6.18 0 0.78 0.63
#> 2 2 Upper 24 288. 142 2.8 0.3 0.67 0.77
#> 3 3 Upper 36 288. 191. 1.97 0.8 0.64 0.73
#> 4 1 Lower 12 288. 61.9 -2.43 0 0.78 0.63
#> 5 2 Lower 24 288. 142 0.93 0.09 0.67 0.77
#> 6 3 Lower 36 288. 191. 1.97 0.2 0.64 0.73
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>- Simulation results based on 10,000 replications.
#> n t events ahr lower upper
#> 7 289 12 62.11 0.81 0.00 0.0
#> 8 289 24 142.28 0.68 0.09 0.3
#> 9 289 36 191.44 0.65 0.20 0.8- Type I error
gsdmvn::gs_power_npe(
theta = rep(0, length(analysisTimes)),
info = x$info0[x$Bound == "Upper"],
upar = x$Z[x$Bound == "Upper"],
lpar = rep(-Inf, 3)
)$Probability[1:length(analysisTimes)]
#> [1] 3.205080e-10 2.555246e-03 2.523428e-02- Compared with fixed design
gsdmvn::gs_design_wlr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
weight = function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0, gamma = 0.5)
},
ratio = 1, alpha = 0.025, beta = 0.2,
upar = -qnorm(0.025),
lpar = -qnorm(0.025),
analysisTimes = 36
)$bounds
#> # A tibble: 1 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 36 261. 173. 1.96 0.8 0.639 0.732
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>7.10 Sample size calculation \(FH(0.5, 0.5)\)
- Sample size
x <- gsdmvn::gs_design_wlr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
ratio = ratio, alpha = alpha, beta = beta,
weight = function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0.5, gamma = 0.5)
},
upper = gs_spending_bound,
lower = gs_spending_bound,
upar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = alpha),
lpar = list(sf = gsDesign::sfLDOF, total_spend = beta),
analysisTimes = analysisTimes
)$bounds %>%
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, digits = 2)
x
#> # A tibble: 6 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 12 304. 65.3 5.05 0 0.79 0.68
#> 2 2 Upper 24 304. 150. 2.51 0.42 0.68 0.93
#> 3 3 Upper 36 304. 201. 1.99 0.8 0.65 0.97
#> 4 1 Lower 12 304. 65.3 -1.8 0 0.79 0.68
#> 5 2 Lower 24 304. 150. 1.12 0.12 0.68 0.93
#> 6 3 Lower 36 304. 201. 1.99 0.2 0.65 0.97
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>- Simulation results based on 10,000 replications.
load("simulation/simu_gsd_wlr_boundary.Rdata")
simu_res %>%
subset(rho == 0.5 & gamma == 0.5) %>%
select(-scenario, -rho, -gamma) %>%
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, digits = 2)
#> n t events ahr lower upper
#> 4 304 12 65.10 0.81 0.00 0.00
#> 5 304 24 149.51 0.68 0.12 0.42
#> 6 304 36 201.23 0.66 0.20 0.80- Type I error
gsdmvn::gs_power_npe(
theta = rep(0, length(analysisTimes)),
info = x$info0[x$Bound == "Upper"],
upar = x$Z[x$Bound == "Upper"],
lpar = rep(-Inf, 3)
)$Probability[1:length(analysisTimes)]
#> [1] 2.209050e-07 6.036759e-03 2.515345e-02- Compared with fixed design
gsdmvn::gs_design_wlr(
enrollRates = enrollRates, failRates = failRates,
weight = function(x, arm0, arm1) {
gsdmvn::wlr_weight_fh(x, arm0, arm1, rho = 0.5, gamma = 0.5)
},
ratio = 1, alpha = 0.025, beta = 0.2,
upar = -qnorm(0.025),
lpar = -qnorm(0.025),
analysisTimes = 36
)$bounds
#> # A tibble: 1 × 11
#> Analysis Bound Time N Events Z Probability AHR theta
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Upper 36 269. 178. 1.96 0.8 0.650 0.973
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: info <dbl>, info0 <dbl>